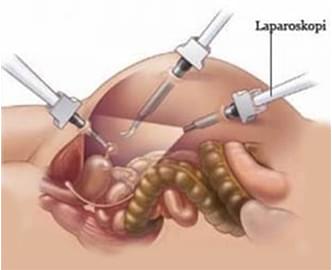
What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that allows access to the abdominal or pelvic organs through small incisions. A camera (laparoscope) and specialized surgical instruments are used to perform the operation. Typically, 3-5 small incisions of 0.5 to 1 cm are made, and trocars (thin tubes) are inserted. The camera and instruments are passed through these trocars to carry out the procedure.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Surgery
-
Cosmetic Appearance: Minimal scarring due to small incisions.
-
Less Pain: Patients experience less postoperative pain compared to open surgery.
-
Faster Recovery: Shorter hospital stays and quicker return to daily activities.
-
Reduced Bleeding: Enhanced visualization allows for better control of bleeding.
-
Educational Ease: Magnified view aids in surgical training and execution.
Applications of Laparoscopic Surgery in Urology
-
Kidney tumor surgeries
-
Removal of atrophic kidneys
-
Kidney cyst removal
-
UPJ obstruction correction surgeries
-
Adrenal gland surgeries
-
Ureter operations
-
Lymph node removal
For prostate and bladder cancer surgeries, open or robotic surgery is preferred over laparoscopic methods.
Complications of Laparoscopic Surgery
As with any surgical procedure, laparoscopic surgery has potential complications:
-
Respiratory Issues: Rare breathing problems due to carbon dioxide insufflation.
-
Position-Related Pain: Postoperative pain related to patient positioning.
-
Conversion to Open Surgery: In some cases, conversion to open surgery may be necessary (approximately 5%).
-
Bleeding: Lower risk of bleeding compared to open surgery.
When performed by experienced surgeons, the complication rates of laparoscopic surgery are significantly low.

