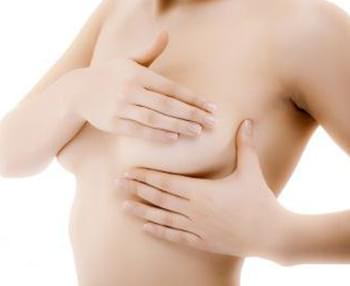
Breast Self-Examination
Regular self-examination of the breasts is the first step in detecting breast cancer at an early stage and initiating timely treatment. Every woman should perform a breast self-exam once a month, ideally 5-7 days after the start of menstruation when hormonal effects are minimal. Through regular self-exams, women become familiar with their breast tissue and can detect new lumps early.
Early signs of breast cancer may not be noticeable. As the disease progresses, changes such as lumps in the breast or armpit, alterations in breast size or shape, nipple discharge, or skin changes on the breast or nipple may occur. While many of these changes are not cancerous, it is essential to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
Mammographic Screening Programs
Why Are They Recommended?
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women. If not detected early, the risk of death increases. Mammography is the most effective method for early detection of breast cancer, capable of identifying tumors approximately two years before they can be felt during a physical exam.
Who Should Undergo Screening?
Even without any symptoms, all women over the age of 40 are advised to have regular mammograms. In countries with regular screening programs, breast cancer mortality rates have decreased by 19-64%.
Who Is Not Recommended for Screening?
Women under 40 are generally not recommended for mammographic screening. This is due to the higher density of breast tissue in younger women, which can reduce the effectiveness of mammography, and increased sensitivity to radiation.
Screening Intervals
For women over 40, mammographic screening can be conducted every one to two years. Annual screening is particularly recommended for women between 40 and 50 years old, as cancers in this age group may grow more rapidly.

